T
S
Strong Customer Authentication
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA)
What is Strong Customer Authentication (SCA)?
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is a regulatory requirement introduced under the European Union's Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) that mandates the use of multi-factor authentication for online payments. To ensure a transaction is compliant, the payer must verify their identity using at least two of the three independent elements of authentication: Knowledge (something the user knows, like a PIN), Possession (something the user owns, like a smartphone), and Inherence (something the user is, like a fingerprint or FaceID). Its primary purpose is to reduce Card-Not-Present (CNP) fraud by ensuring that the person initiating the transaction is the legitimate cardholder.
Deep Dive: The Mechanics of Verification
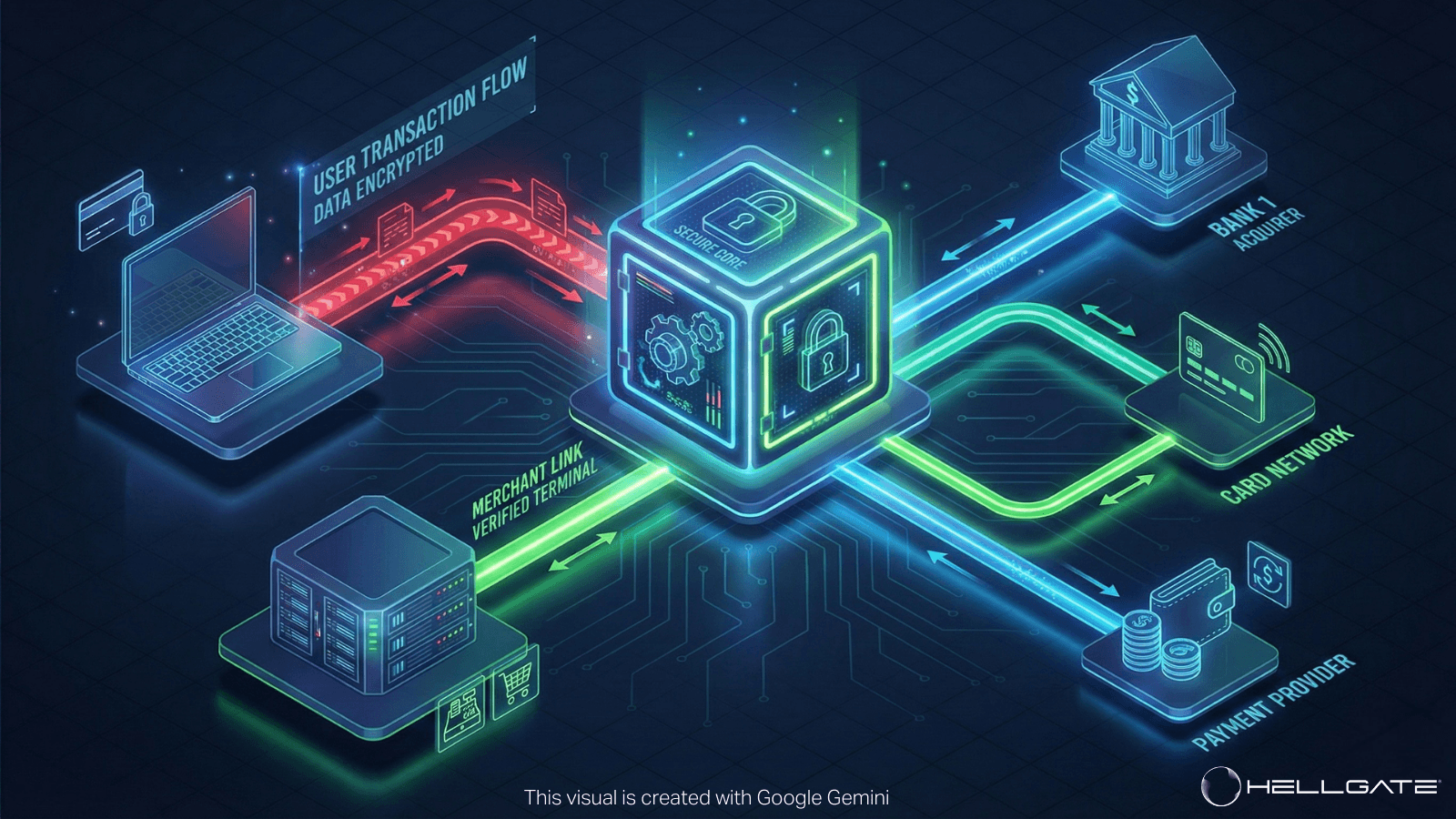
While SCA is the regulation, the mechanism used to enforce it in the card payment world is typically 3D Secure 2.0 (3DS2).
1. The Three Pillars of Authentication
For a transaction to pass SCA checks, the authentication flow must combine two distinct categories. Using two from the same category (e.g., a Password and a PIN) is not compliant.
Knowledge (Something you know): A password, PIN, passphrase, or secret answer.
Possession (Something you have): A mobile device (verified via SMS OTP or app push notification), a smart card, or a hardware token generator.
Inherence (Something you are): Biometric data such as a fingerprint scan, facial recognition (FaceID), voice recognition, or iris scan.
2. Technical Mechanics: The 3DS 2.0 Flow
The modern implementation of SCA utilizes the EMV® 3-D Secure protocol to minimize user friction.
Data Exchange: When the customer clicks "Pay," the merchant sends over 100 data points (device ID, shipping history, browser info) to the Issuer via the 3DS server.
Risk Analysis: The Issuer performs a "Frictionless Flow" analysis. If the data strongly indicates the user is legitimate (e.g., same device, typical location), the Issuer may grant an exemption.
The Challenge (If needed): If the risk score is high, the Issuer triggers a "Challenge Flow." The customer is presented with a modal window requiring them to authenticate (e.g., enter an SMS code or scan their face in their banking app).
Authorization: Once authenticated, the transaction proceeds to standard authorization with a "Liability Shift"-meaning the Issuer, not the merchant, is liable for fraud.
3. Strategic Importance
Compliance is Mandatory: For merchants processing transactions where both the issuer and acquirer are in the European Economic Area (EEA), SCA is non-negotiable. Non-compliance results in "Soft Declines" (Issuer rejection).
Liability Shift: Successfully performing SCA shifts the financial liability for chargebacks (specifically "Fraud" reason codes) from the merchant to the issuing bank.
Trust Signals: In an era of high cybercrime, visible security challenges (like biometric prompts) can paradoxically increase consumer trust in the platform.
4. Comparison: SCA vs. 2FA
Feature | Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) |
Scope | General security term. | Specific Legal/Regulatory Requirement (PSD2). |
Independence | Factors may be linked. | Factors must be strictly independent (breach of one does not compromise the other). |
Dynamic Linking | Not required. | Dynamic Linking required (The code generated must be specific to the amount and payee). |
Applicability | Logins, access control. | Payments, accessing financial data. |
Common Pain Points of SCA
The introduction of SCA created a significant friction point in e-commerce known as "Conversion Drop-off."
Friction-Heavy Checkout: Being forced to find a phone to read an SMS code interrupts the purchase flow, leading to cart abandonment.
Exemption Management: Complexity arises in identifying which transactions don't need SCA (e.g., Low Value Transactions under €30, Recurring Payments).
Regional Fragmentation: While an EU directive, interpretation varies. The UK (post-Brexit) has its own timeline, and specific national regulators may enforce rules differently.
The Hellgate Approach
Hellgate Guardian transforms SCA from a conversion killer into a seamless security asset.
Unified 3DS Engine: Guardian integrates a native 3D Secure 2 component. It handles the complexity of communicating with the Directory Servers (Visa/Mastercard) and the Access Control Servers (Issuers). You trigger one API call, and Guardian manages the iframe or mobile SDK challenge.
Exemption Optimization: Guardian works with Hellgate Hub to flag transactions eligible for exemptions (TRA - Transaction Risk Analysis). If a transaction is low risk, Guardian requests a "Frictionless" auth. If the bank declines the exemption, Guardian automatically retries with the Challenge flow (Soft Decline recovery).
Decoupled Authentication: By handling SCA within the Guardian vault environment, the authentication token is bound to the secure payment data, ensuring that even if the customer is challenged, the raw card data remains protected and out of your scope.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Does SCA apply to US transactions?
A: Generally, no. SCA applies to "Two-Leg" transactions where both the Merchant's Acquirer and the Customer's Issuer are in the EEA/UK. However, global merchants selling to EU customers must comply if they use a local EU acquirer.
Q: What is "Dynamic Linking"?
A: A crucial element of SCA. The authentication code generated (e.g., the SMS OTP) must be mathematically linked to the specific transaction amount and the specific payee. If the amount changes, the code becomes invalid.
Q: Are subscriptions exempt from SCA?
A: The first transaction (when the card is stored) requires SCA. Subsequent "Merchant Initiated Transactions" (MITs) for recurring billing are exempt, provided the initial mandate was properly authenticated.
Q: What happens if I don't implement SCA?
A: Issuers will systematically decline your transactions with specific error codes indicating that strong authentication is required. You will lose 100% of your European traffic.